1. Introduction to Sports Medicine Billing in 2025
Sports medicine is a specialty experiencing rapid growth. With rising patient volumes, more complex injuries, and tighter payer rules, clinics are facing significant billing and coding challenges. In 2024, over 22 million Americans received treatment for sports-related injuries, and the numbers are expected to increase in 2025.
Clinically, this growth is positive. Financially, it can be a minefield. Sports medicine billing involves multiple service types—E/M visits, imaging, procedures, DME, and physical therapy. Each comes with specific coding rules, documentation requirements, and payer idiosyncrasies. Without a robust billing strategy, clinics can lose 15–25% of revenue to denials, underpayments, and missed charges.
This guide breaks down the 2025 sports-medicine billing landscape, CMS updates, and practical steps to optimize revenue while staying compliant.
2. Why Sports Medicine Billing Has Become More Complex
2.1 High Patient Volume and Injury Variability
Every day in sports medicine is unique. Clinics handle sprains, fractures, tendon injuries, post-surgical rehab, and return-to-play assessments. Each case has its own coding pathway, which increases denial risk.
2.2 Therapy Documentation Challenges
Payers heavily scrutinize physical therapy (PT) and occupational therapy (OT). Key documentation requirements include:
- Measurable progress
- Functional testing results
- Clear treatment goals
- Time-based therapy documentation
Incomplete therapy notes often lead to claim denials.
2.3 DME Audit Risk
Durable Medical Equipment (DME) billing—braces, orthotics, crutches—requires:
- Proof of medical necessity
- Written orders
- Correct HCPCS codes and modifiers
- Prior authorization when needed
Many payers downcode DME silently, causing hidden revenue loss.
2.4 Modifier-Driven Denials
Same-day E/M and procedural visits must use modifier 25; otherwise, claims may be rejected. Using incorrect modifiers (-25, -59, -26/TC) remains one of the top denial drivers.
2.5 Payer Variability
Medicare, Medicaid, commercial insurance, and workers’ compensation each have distinct rules for:
- Coverage limits
- Documentation requirements
- Bundling edits
Sports medicine billing is not generic outpatient billing; it’s a complex, specialty-specific domain.
3. 2025 Regulatory Landscape for Sports Medicine Providers
3.1 CMS Updates
The 2025 CMS Physician Fee Schedule introduces:
- Conversion factor: $32.36, down from $32.74 in 2024
- Adjusted RVUs for high-volume musculoskeletal procedures
- Tighter documentation rules for therapy codes
- Updated DME documentation and audit requirements
3.2 Commercial Payer Tightening
Private insurers are increasingly scrutinizing:
- Therapy progress notes
- Imaging medical necessity
- Procedure documentation and bundling
3.3 Workers’ Comp Changes
Workers’ compensation claims now require:
- Enhanced verification
- Pre-authorization for high-cost procedures
Clear documentation for repeat or post-surgical therapy.
4. Core Components of Sports Medicine Billing
4.1 E/M Coding
Common codes: 99202–99215. Clinics must document:
- Medical decision-making (MDM) or time-based E/M selection
- Tests ordered and results
- Justification for same-day procedures using modifier 25
4.2 Procedure Coding
Includes injections, arthroscopy, tendon repairs. Tips:
- Use correct CPT codes (e.g., 20610, 20550/20551)
- Document laterality, approach, and anesthesia
- Apply modifier 59/XS for distinct procedural services.
4.3 Imaging Billing
Key codes: 73560 (knee X-ray), 73721 (MRI). Ensure:
- Medical necessity documentation
- Prior conservative care evidence
- Correct POS and CPT/HCPCS codes
4.4 Therapy & Rehabilitation Billing
Timed codes require:
- Measurable functional goals
- Progress documentation
- Compliance with Medicare 2025 therapy rules
4.5 DME Billing
HCPCS codes like E1399 or Lxxxx must include:
- Supplier enrollment verification
- Medical necessity orders
Modifier NU for new equipment.
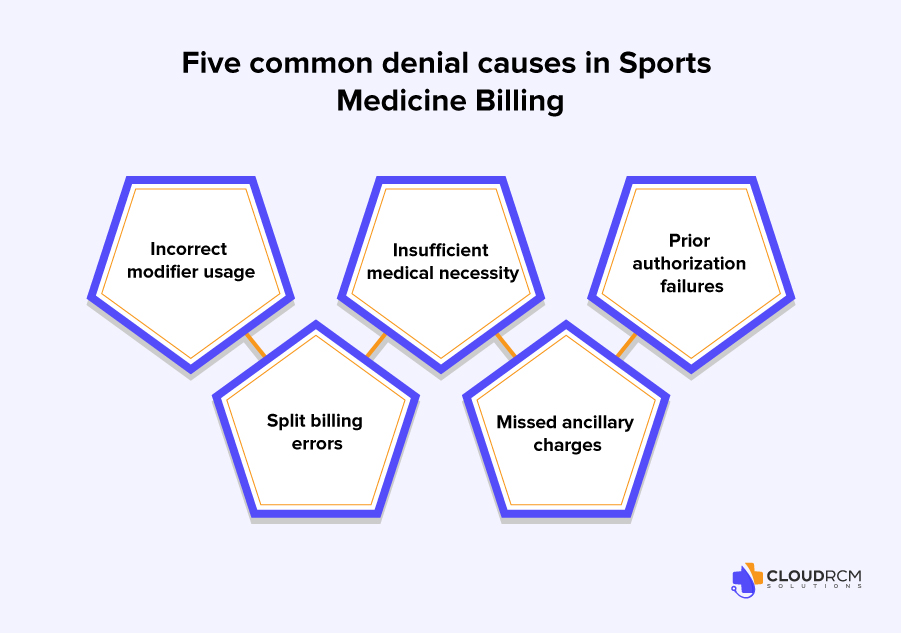
5. Most Common Denials in Sports Medicine
- Incorrect modifiers (-25, -59, 26/TC)
- Insufficient medical necessity for imaging/procedures
- Prior authorization failures
- Split billing errors (professional vs technical)
- Missed ancillary charges (braces, orthotics, injectables)
6. Revenue Loss Areas & Root-Cause Analysis
| Problem | Why it Hurts Revenue | Solution |
| Wrong CPT/ICD pairing | Leads to claim rejection | Use audit-ready coding workflow |
| Missing modifiers | Denial of E/M + procedure | Modifier training & auto-checks |
| Weak therapy documentation | Denied sessions | Structured templates |
| DME billed incorrectly | Claim rejection or downcoding | Verify orders, codes, auth |
| Missed charges | Lost revenue | Charge capture tied to EHR |
| Slow follow-up | Timely filing limits hit | Dedicated AR follow-up |
| No patient collections workflow | Uncollected coinsurance | Upfront collection system |
7. Best Practices for Sports Medicine Billing 2025
7.1 Authorization Workflow
- Pre-check eligibility and prior authorization for:
- MRIs
- Ultrasounds
- Injections
- DME
- Therapy sessions
7.2 Documentation Standards
- Therapy: time, goals, progress, functional scores
- Procedures: laterality, site, findings, imaging
- DME: orders, diagnosis, clinical notes
7.3 Modifier Accuracy
- 25 – E/M + procedure same day
- RT/LT – laterality
- 59 – distinct services
- 76/77 – repeat services
7.4 Therapy Compliance Audits
- Monthly therapy audits prevent denials.
- Capture therapy time accurately.
- Document progress toward goals.
7.5 Charge Capture Protocols
- Track all supplies (braces, slings, boots, tapes)
- Tie charges to encounters in EHR
- Submit claims within 24–48 hours
- Follow up on denials within 7–14 days
Collect patient responsibility upfront.
8. CMS 2024–2025 Fee Schedule Update: Impact on Sports Medicine
- Conversion factor: $32.36 (down 1.2%)
- High-use orthopedic procedures: minor RVU adjustments
- Therapy billing: stricter timed-code documentation
- DME: increased prior authorization and documentation requirements
- Imaging: heightened audit scrutiny
Impact: Clinics must optimize coding, documentation, and charge capture to prevent revenue loss.
9. How Modern RCM Improves Sports Medicine Financial Health
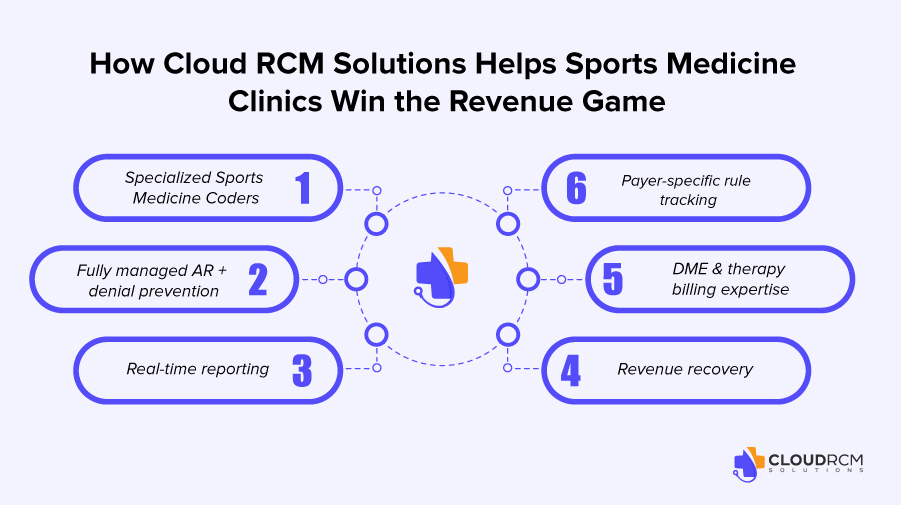
Cloud RCM Solutions provides:
- Specialized sports-medicine coders
- Payer-specific rule tracking (Medicare, Medicaid, commercial, workers’ comp)
- Fully managed AR and denial prevention
- DME & therapy billing expertise
- Real-time dashboards for denial trends, cash flow, payer mix, CPT utilization, and missing charges
Revenue recovery (10–18% hidden charges often found)
Conclusion
Sports medicine is growing rapidly, but so are payer demands. Clinics need:
- Accurate coding and documentation
- Fast, compliant RCM processes
- Modifier checks and therapy audits
- DME and ancillary charge capture
- Proactive AR and denial management
Cloud RCM Solutions provides the tools, expertise, and workflow integration needed to maximize revenue, reduce denials, and keep your clinic financially healthy in 2025.
FAQs
What is sports medicine medical billing?
It’s the process of coding, submitting, and managing claims for sports injuries, orthopedic treatments, rehab, and athletic procedures.
Why do sports medicine claims get denied often?
Most denials happen due to missing documentation, incorrect CPT/ICD-10 codes, or payer-specific medical necessity rules.
Which codes are most used in sports medicine billing?
Common codes include E/M visits, musculoskeletal injury codes, physical therapy CPTs, and ultrasound-guided injection codes.
Do sports medicine procedures require prior authorization?
Yes, MRIs, PRP therapy, injections, and advanced imaging usually need PA depending on the payer.
How does Cloud RCM Solutions help sports medicine practices?
By managing coding accuracy, eligibility checks, denial prevention, and payer-specific workflows.
Can athletic trainers and PT services be billed separately?
Only if payers allow distinct, medically necessary services with proper documentation and modifiers.
How can practices increase reimbursement for sports injury treatments?
Use correct modifiers, verify benefits upfront, and document medical necessity clearly.
What are the CMS 2025 updates affecting sports medicine?
Lower conversion factor, updated RVUs for procedures, stricter therapy documentation, DME audits, and imaging review.
How to reduce denials in sports medicine billing?
Pre-authorize services, audit documentation, use correct modifiers, track DME, and submit claims promptly.
What are common revenue leaks in sports medicine?
Missed charges, weak documentation, wrong modifiers, DME errors, unbilled supplies, and slow follow-up.

 Medical Billing
Medical Billing Medical Coding
Medical Coding Medical Audit
Medical Audit Provider Credentialing
Provider Credentialing Denial Management
Denial Management A/R Follow-up
A/R Follow-up Private Practice
Private Practice Patient Help Desk
Patient Help Desk Customized Reporting
Customized Reporting Out-of-Network Billing
Out-of-Network Billing Internal Medicine
Internal Medicine Pediatrics
Pediatrics Radiology
Radiology Surgery
Surgery Emergency Medicine
Emergency Medicine Anesthesiology
Anesthesiology Cardiology
Cardiology Orthopedic
Orthopedic Psychiatry
Psychiatry Dentistry
Dentistry OB-GYN
OB-GYN Family Medicine
Family Medicine


